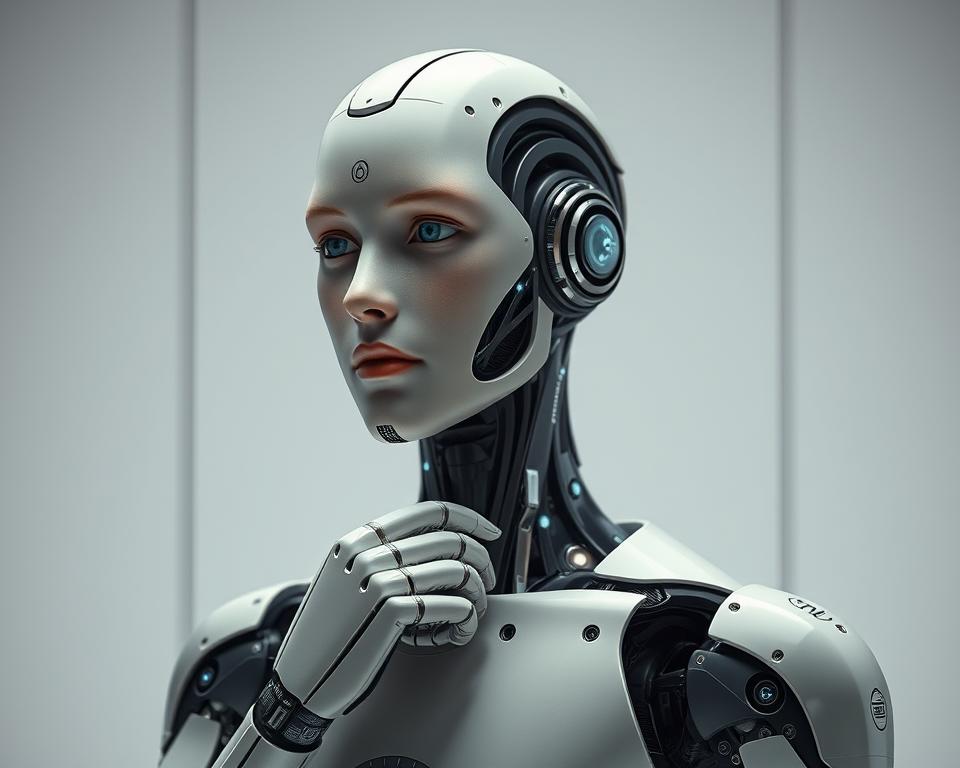
Can a robot truly feel empathy like a human? Companies like Hanson Robotics and Realbotix are making big strides. They’re creating robots like Sophia, with AI and realistic faces, and Aria, for natural interactions. The difference between humans and machines is getting smaller.
Today’s robots are more than tools; they’re becoming friends. Engineers use AI, sensors, and materials to make robots that move, talk, and even feel. This mix of tech and art aims to tackle big problems, like helping in healthcare and customer service. But, these advanced robots also bring up big questions about ethics, identity, and how we’ll interact with them in the future.
Key Takeaways
- Human-like robots like Sophia and Aria showcase AI advancements in movement and communication.
- Human-inspired AI merges robotics with fields like biomechanics and material science.
- These technologies raise debates about trust, ethics, and societal impact.
- Companies like Honda and Realbotix lead in creating lifelike robots for real-world use.
- Public perception and cultural acceptance shape how these innovations develop globally.
Introduction to Human-Like Robots
Humanoid robots combine human design with cutting-edge tech for tasks that need interaction and movement. They are made to look and act like humans, with features like limbs and faces. This lets them move around in spaces made for people.
Definition and Overview of Humanoid Robotics
Humanoid robotics aims to create robots that look and act like humans. Robots like Sophia from Hanson Robotics and NAO by SoftBank are examples. They use sensors and AI to mimic human gestures and speech.
Historical Evolution of Human-Like Robots
The first robots, like Honda’s ASIMO from 2000, were made for disaster work. Today, robots like Sophia have even been given citizenship in Saudi Arabia in 2017. Each step forward shows better motor skills and thinking abilities.
Key Technologies Driving Human Similarity
- Sensors: Cameras and touch systems for knowing the environment.
- AI Learning: Neural networks help with speech and making choices.
- Biomechanics: Joint systems for smooth, natural movements.
These advancements are making robots more like humans. They’re changing fields like healthcare and education.
The Science Behind Lifelike Motion
The science of lifelike motion in AI robots combines engineering with human anatomy. Engineers use advanced algorithms to make robots move like us. This lets them walk, reach, and balance just like humans.
Advancements in Robotics Mobility
Recent breakthroughs have made robots better at moving around. Key technologies include:
- Inverse kinematics (IK) solvers figure out joint angles for precise limb movements.
- Path planning algorithms help robots avoid obstacles in real time.
- Dynamic stabilization keeps robots upright during motion.
Role of Biomechanics in Movement Simulation
Biomechanics studies human joints and muscles to help design robots. For example, Sophia the AI robot uses spring-loaded actuators to mimic human leg flexion. Researchers also study spinal curvature to improve upper-body gestures.
These innovations help robots move smoothly between walking, crouching, and climbing. Dynamic models now simulate muscle-tendon interactions, making movements less jerky. Tests show robots can adapt better in uneven terrain, moving more naturally like humans.
Artificial Intelligence and Human Interaction
Artificial intelligence is changing how human-like robots talk to us. They use natural language and emotions to connect with us. Companies like Realbotix and Hanson Robotics are leading this change. They aim to make robots that feel like friends.
Natural Language Processing in Robots
Natural language processing (NLP) lets human-like robots understand and speak like us. Realbotix’s Aria model uses AI to get what we mean and talk back in a way that feels right. This tech helps robots help us, answer questions, and chat easily.
- Speech recognition: Accurately capturing user input
- Context analysis: Understanding tone and intent
- Dynamic response: Generating fluid, relevant replies
Emotional Intelligence in Humanoid AI
Emotional intelligence in AI makes robots seem to care and understand us. Hanson Robotics’ Loving AI lets robots read our faces and act right. They can even comfort us when we’re upset or happy with us.
These robots learn from us to get better at showing emotions. This is key in places like hospitals, schools, and shops where feeling understood is important.
Notable Examples of Human-Like Robots
Advanced robotics has led to the creation of robots that look and act like humans. These robots show off the latest in engineering and AI. They are changing what we think machines can do.
Sophia: A Pioneer in Human-Like Robotics
Sophia was made by Hanson Robotics and is the first robot to get citizenship. She can show 62 different expressions on her face, thanks to AI. In 2023, Sophia joined global talks, showing how robots can help in diplomacy and learning.
Asimo: Honda’s Engineering Marvel
Asimo, from Honda, was introduced in 2000. It can walk, run, and balance at 3.7 mph. It uses sensors to move around safely. Over 20 years, Asimo has grown from a simple robot to a tool for helping in emergencies and healthcare.
Geminoid: The Ultra-Realistic Android
Hiroshi Ishiguro created Geminoid robots. They look and move like humans, thanks to their silicone skin and sensors. The newest Geminoid, DK, can understand voice commands and mimic gestures. These robots help scientists study how humans interact with robots.
| Robot | Creator | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Sophia | Hanson Robotics | Emotional expression AI |
| Asimo | Honda | Dynamic mobility |
| Geminoid | Ishiguro Lab | Biomimetic design |
Applications of Human-Like Robots
Humanoid technology is changing industries in big ways. It’s used in hospitals and stores to solve real problems. These robots can interact like humans, making tasks more efficient and caring.
Healthcare and Assisted Living
In healthcare, humanoid robots help with patient care and support for the elderly. Robots like Pepper assist in physical therapy, helping patients move better. They also remind seniors to take their medicine and check their health, easing the burden on caregivers.
Nursing homes use these robots to keep residents engaged. They offer interactive programs that act as companions, improving life for seniors.
Customer Service and Retail Solutions
Retail stores use humanoid technology to make things run smoother. Best Buy, for example, has robots that help customers, answer questions, and handle payments. This cuts down wait times and helps manage stock better.
In malls, humanoid assistants guide shoppers to what they need. This real-time help boosts customer happiness.
Companionship and Social Robots
Social robots fight loneliness by being friends. Paro, a seal-like robot, comforts patients with dementia. Sony’s Aibo robotic dog offers emotional support by acting like a real pet.
These robots use humanoid tech to connect with people. They help with mental health in places where people often feel alone.
Ethical Considerations in Robotic Development
Robotics innovation raises big ethical questions. Machines like Sophia show advanced interaction, sparking debates. People wonder if AI should have rights or be considered “people.”
Researchers are looking into if advanced systems can become conscious. This makes policymakers think about creating AI welfare frameworks.
AI Rights and Personhood
“If AI achieves sentience, we must redefine ethical boundaries.” — Dr. Kate Darling, MIT Media Lab
There’s a big debate between philosophers and engineers. They disagree on whether robots should be treated with moral respect. Studies show up to 47% of U.S. jobs could be at risk.
But, when AI systems seem to show empathy, it gets tricky. The EU’s proposed AI Act sees advanced systems as high-risk. This shows a shift in how we might regulate AI.
Employment and Economic Shifts
- White-collar roles in tech and finance face 23% higher automation risk than manual jobs
- San Francisco and New York top cities at risk, with legal and creative sectors most affected
- Global translation markets see a 15% drop in human linguists as AI tools like DeepL dominate
Robotics innovation could widen the gap between rich and poor. Unless education changes, it might make things worse. Programs to teach AI maintenance and ethics could help, but policy is slow to catch up.
Public Perception of Human-Like Robots
As AI robot design gets better, people feel both excited and cautious. Surveys show people are eager for robots to help in healthcare but worry about ethics and jobs. Seeing robots like Sophia on TV or Aria at CES changes how we think about them.
Survey Insights: Acceptance and Concerns
- 68% of US adults (Pew Research 2023) think AI robot design could help the elderly but worry about losing jobs.
- 43% of people at the 2024 robotics summit found robots like Geminoid a bit scary because they look so human.
Media Influence on Public Opinion
Shows like Westworld and Ex Machina mix reality and fiction. When Honda’s Asimo danced on The Tonight Show, it started a big online talk about friendly AI robot design. But scary movies make people doubt robots.
“Media exposure is a double-edged sword. Positive portrayals inspire innovation, but exaggerated fears can stall progress.” – Robotics Ethics Panel 2024
How people feel about robots depends on where they are used. Robots in healthcare are seen as helpful, but those in policing raise doubts. Designers, like Sony with Aibo, try to make robots look friendly. Finding the right balance between new and familiar is crucial for acceptance.
Future Trends in Humanoid Robotics
Human mimicry robots are set to change industries with new tech. Advances in AI and engineering will make them more like humans. This will change how they interact with us.

Expected Technological Innovations
Developers are working hard to make human mimicry robot systems better. They want them to be more realistic and useful. Here are some key areas:
- Advanced Motion Control: They will move like humans, with gestures and expressions.
- AI Integration: They will learn and adapt quickly to new situations and people.
- Material Science: They will be made of lightweight, strong materials for long use in many places.
Potential Market Growth and Developments
The market for humanoid robots is expected to grow fast. MarketsandMarkets says it could hit $30.1 billion by 2030. The main reasons are:
| Year | Projected Revenue |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $8.2 Billion |
| 2025 | $14.5 Billion |
| 2030 | $30.1 Billion |
Companies like Tesla’s Optimus and new models for CES 2024 are leading this growth. These robots will work in healthcare, manufacturing, and more. They will focus on making interactions with humans easier and more natural.
The Role of Robotics in Education
Robotic technology is changing classrooms into lively learning areas. Schools globally use robots like NAO and Pepper to make learning fun and interactive. These tools help explain complex ideas and boost creativity and technical skills.
Robots as Learning Assistants
Robots serve as personal tutors, helping students through lessons. NAO robots help with language by practicing vocabulary. Pepper robots in libraries make finding books a fun task. A 2023 study found:
Students using robots showed a 25% improvement in math problem-solving skills.
Teaching STEM Concepts with Robotics
Robots make abstract ideas real through hands-on projects. Building and programming robots teach coding and engineering. Here are some examples:
| Robot Model | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| NAO | Science demonstrations | Visualization of physics concepts |
| Pepper | Math tutoring | Adaptive learning paths |
| LEGO Mindstorms | Robotics clubs | Collaborative project-based learning |
These tools get students ready for careers in tech. Schools working with companies like SoftBank (Pepper) see more interest in STEM subjects. Robotic technology is becoming a key part of today’s classrooms.
Human-Robot Collaboration in the Workplace
Workplaces are changing as humans and robots work together. Collaborative robots, or cobots, help in making, moving goods, and in healthcare. They make work smoother and let people do creative and strategic tasks. Projects like Apptronik’s Apollo show how these teams boost accuracy and cut down mistakes.
Enhancing Productivity through Collaboration
Robots take over repetitive tasks, making work more efficient. In car factories, cobots put parts together quickly, saving 20% or more of time. This lets people focus on checking quality or helping customers. The main advantages are:
- Manufacturing: Faster production cycles
- Logistics: Real-time inventory tracking
- Healthcare: Surgical precision support
Addressing Challenges in Human-Robot Teams
But, there are hurdles like safety and getting used to new ways of working. A 2023 report found three main problems and how to solve them:
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Safety protocols | AI-driven collision detection systems |
| Workflow adaptation | Phased training programs for staff |
| Trust in automation | Transparent AI decision-making processes |
Getting robots and humans to work well together needs constant talk between tech experts and workers. Making sure safety and flexibility are key helps teams work better together.
Research Frontiers in Humanoid Robotics
Humanoid robotics research is moving forward thanks to interdisciplinary robotics research. This combines engineering, AI, and cognitive sciences. At places like Hanson Robotics and Arizona State University’s CHART, teams from different fields work together. They tackle tough design problems to make robots that can learn, adapt, and interact better with humans.
Interdisciplinary Approaches to Robotic Design
For humanoid robotics collaboration to succeed, you need a mix of skills. Key areas include:
- Engineering: Making mechanical systems and motor control better
- Artificial Intelligence: Improving algorithms for robots to make decisions
- Cognitive Science: Helping robots understand social cues and emotions
A study by the CHART team shows that working together across fields speeds up progress in human-robot teamwork.
Emerging Materials and Sensor Technology
New sensor technology and materials science are key to progress. Things like flexible sensors and light materials help robots move safely and naturally.
| Material | Application |
|---|---|
| Soft polymers | Flexible joints for lifelike movements |
| Pressure-sensitive skins | Enhanced tactile feedback |
| Self-healing composites | Extended durability in dynamic settings |
These advancements focus on safety and flexibility. They’re crucial as humanoid robots start working in healthcare, education, and service. By combining different fields, robots are becoming reliable helpers in our daily lives.
Cultural Differences in Robotic Acceptance
Countries have different views on humanoid robots, influenced by their history and values. Japan sees robots as part of everyday life, while the U.S. worries about ethics.
Japan’s Embrace of Humanoids
In Japan, robots like SoftBank’s Pepper are everywhere. Stories in manga and anime show robots as friends, not foes. This view encourages companies to make robots for care and disaster relief.
- Japan’s robotics market grew 14% in 2022 (Source: Nikkei Asia)
- Pepper robots help seniors in 80% of Tokyo care facilities

American Skepticism Toward AI
In the U.S., 60% fear AI will take jobs. Shows like Black Mirror and Westworld make AI seem scary. This fear slows down the use of robots in healthcare.
A 2023 Pew Research report found 55% of Americans distrust AI’s societal impact
- U.S. robotics startups focus on industrial uses over humanoid forms
- Public forums debate “robot rights” more than practical uses
Japan values humanoid robots for companionship, while the U.S. focuses on AI ethics. Companies worldwide must understand these cultural differences to succeed.
The Impact of Robotics on Daily Life
Human-like robots are now a reality, not just in movies. They could change our daily lives in big ways. They promise to make our routines more efficient and comfortable.
How Human-Like Robots Might Change Society
Picture waking up to a robot adjusting your home’s temperature or reminding you of plans. These robots could take over tasks like cooking and cleaning. This would give us more time for things we enjoy.
Robots could also improve social interactions. They might help care for the elderly or reduce loneliness in homes.
Innovations in Smart Home Integration
Smart homes already use voice-activated systems like Alexa or Google Home. Adding humanoid robots to these systems opens up new possibilities. For instance, a robot could control your smart locks, cameras, and appliances, making your home more connected.
Features like voice-activated scheduling or real-time alerts could become common. This would make managing your home easier than ever.
Experts say robots will work well with our current technology. Key areas include:
- Automated energy management
- Personalized health monitoring
- Adaptive lighting and climate control
Using these technologies raises concerns about privacy and how dependent we might become. But their potential to make our lives simpler is very exciting.
Conclusion: Looking Ahead in Human-Like Robotics
Humanoid robotics is at a turning point. Advances in AI and biomechanics have made robots like Sophia and Asimo key in healthcare and education. But, we must balance progress with ethics.
Summary of Current Trends and Future Prospects
Robots now help in surgeries, guide customers, and offer companionship. Improvements in AI and emotional intelligence are making robots more human-like. Future advancements could lead to smarter robots for elder care or advanced manufacturing, changing industries worldwide.
Call to Action for Responsible Development
As humanoid tech advances, developers must focus on transparency and safety. It’s crucial for policymakers, engineers, and communities to work together. We need to address job loss and ensure AI respects our values. Responsible innovation means creating robots that improve our lives without harming our privacy or dignity.
FAQ
What defines a human-like robot?
A human-like robot, or humanoid robot, looks and acts like a person. It uses advanced tech to move and act like us. This makes it seem very real.
How have human-like robots evolved over time?
At first, these robots were just ideas without real function. Now, thanks to new tech, we have robots like Sophia and Asimo. They show how design and engineering can come together.
What technologies enable robots to achieve lifelike movement?
Advanced sensors and AI help robots move like us. They use biomechanics and simulation to walk and move in a way that feels natural.
How does artificial intelligence enhance human-robot interactions?
AI lets robots understand and speak like us. It also helps them seem to care about how we feel. This makes talking to robots feel more natural.
What are some notable examples of human-like robots?
Sophia is famous for talking like a person. Asimo shows off how robots can move. Geminoid looks so real, it’s almost like a person.
In which sectors are human-like robots being utilized?
Robots like these help in healthcare and retail. They also make good companions. They’re useful in many places.
What ethical considerations arise from developing humanoid robots?
Making robots raises big questions. We wonder if they should have rights or if they could replace jobs. These are important issues as we keep making robots.
How does the public perceive human-like robots?
People have mixed feelings about these robots. Some like the idea, while others are unsure. What they think often depends on what they see in the media.
What future trends are expected in humanoid robotics?
We expect to see robots get even better. More money for research will help. New robots will change how we work and live.
How can humanoid robots enhance education?
Robots can help teach hard subjects in a fun way. They make learning hands-on. This could change how we teach.
What challenges exist when integrating humanoid robots into the workplace?
Robots need to work well with people. We also have to think about safety and trust. It’s not always easy.
What ongoing research is being done in the field of humanoid robotics?
Scientists are working on making robots better. They’re looking at new materials and ways to make robots more useful. This will help robots do more things for us.
How do cultural attitudes impact the acceptance of humanoid robots?
Different cultures see robots in different ways. Japan is more open to them, while the US is more cautious. What we see in the media plays a big role.
What implications does the deployment of human-like robots have on everyday life?
Robots could change how we live and interact. They could make our homes smarter and help us in many ways. This could change how we see the world.